
Ozone, also known as activated oxygen, is a naturally occurring compound that plays an essential role in protecting our planet from the Sun's UV radiation.1 On the ground, its uses in addressing harmful contaminants in various industries are abundant.
From breathable air to a bacteria-killing compound
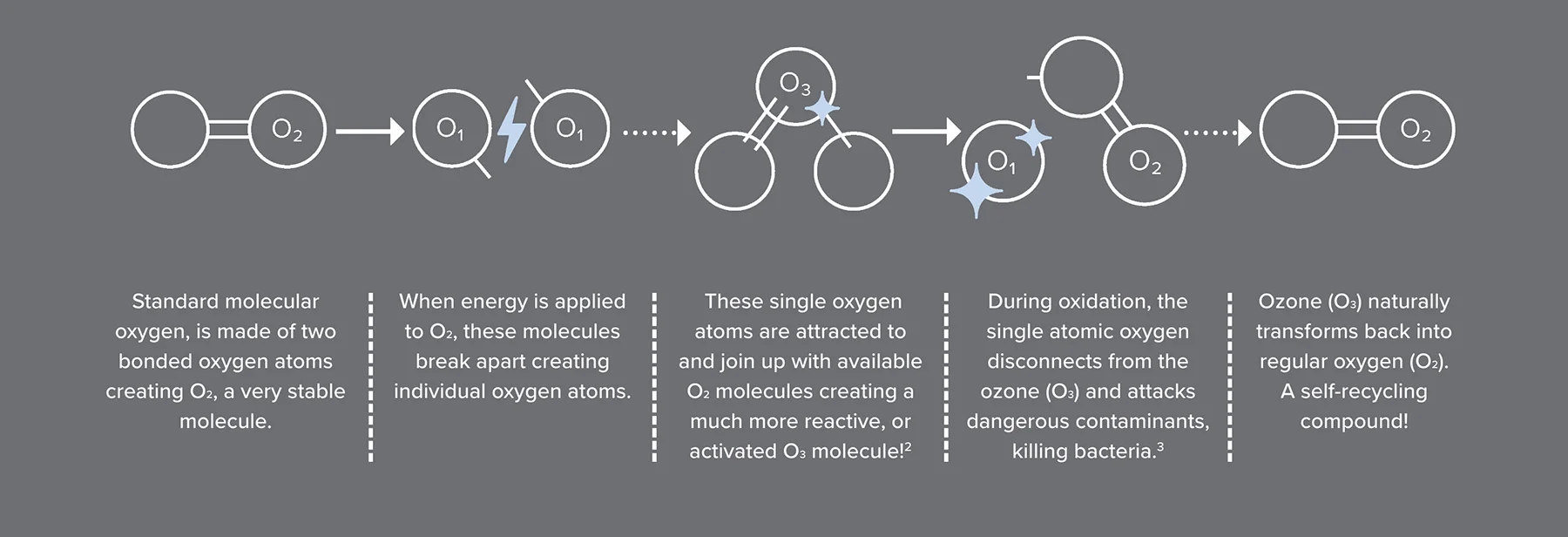
Two oxygen atoms, joined together (O2), is the oxygen we breathe every day. But when three atoms join together, the result is ozone or activated oxygen.


Nature's Cleanser, Reimagined for CPAP Care
The same compound trusted in industries that demand extreme cleanliness is now designed for home use with SoClean 3+.

SoClean 3+ uses Ozone (O3) — a naturally occurring form of oxygen — known for its bacterial reduction power.

It penetrates deep into CPAP accessories, targeting bacteria that linger in hard-to-reach areas.
How Ozone Works With SoClean 3+
SoClean 3+ harnesses faster, better ways to deploy ozone, utilizing Ozone Stream technology to create a powerful ozone mixed with ultra-fine mist, that quickly penetrates even the hardest-to-reach accessory parts, reducing 99.9% of bacteria.
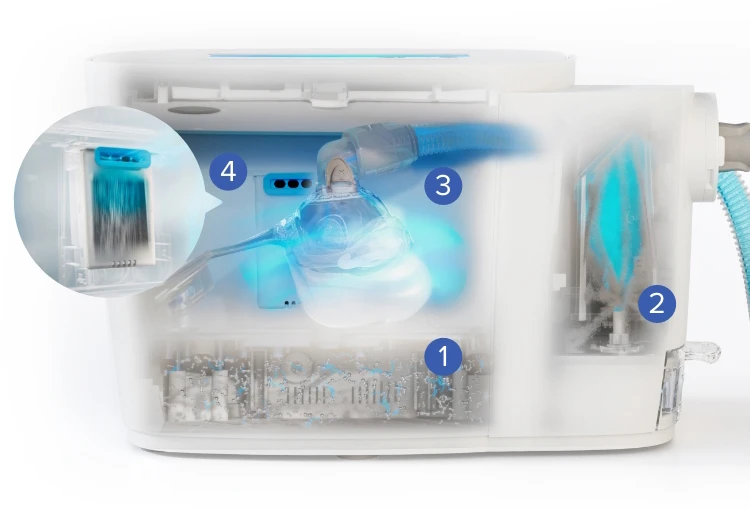
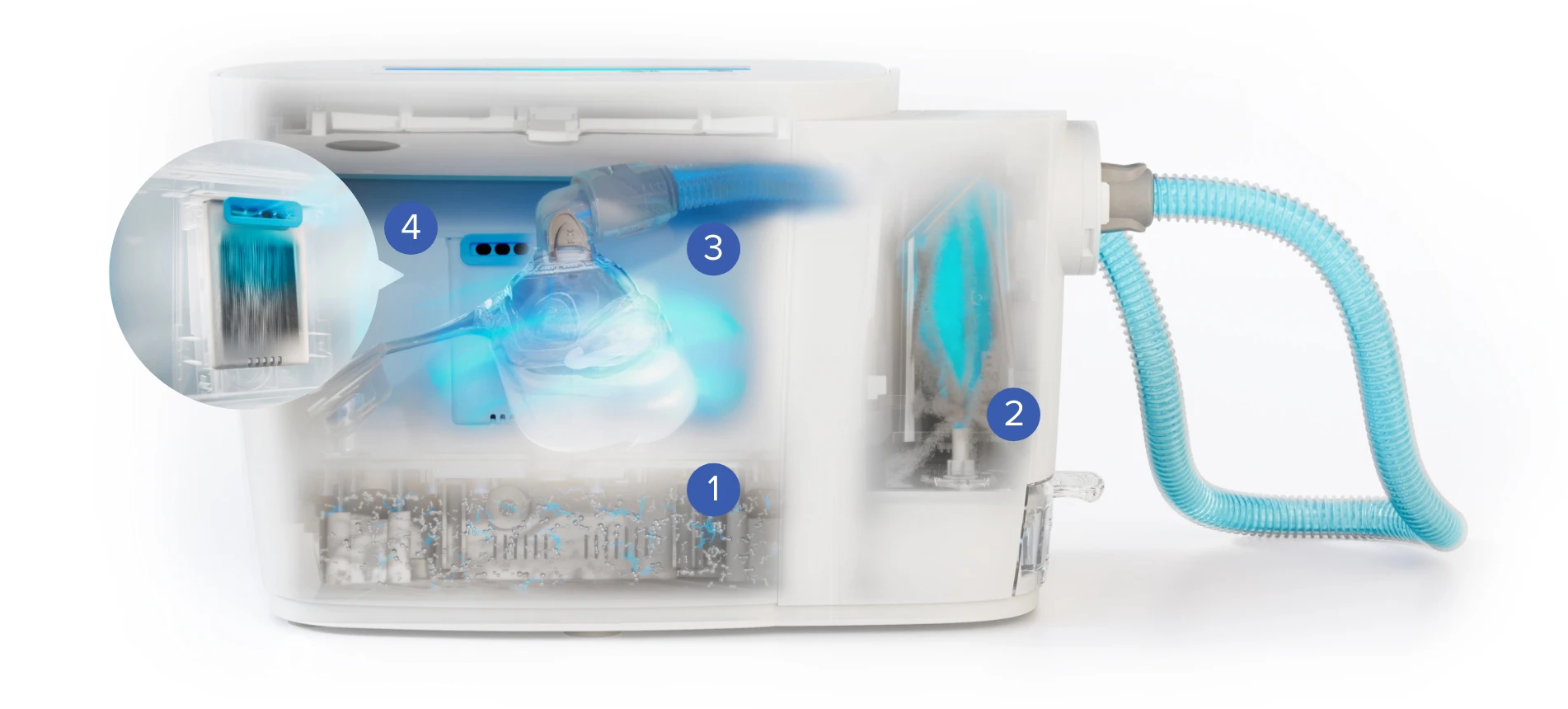

 Generate Ozone
Generate Ozone
 Create Ozone Stream
Create Ozone Stream
 Reduce 99.9% of Bacteria
Reduce 99.9% of Bacteria
 Ozone to Oxygen Acceleration
Ozone to Oxygen Acceleration
Trusted World-Class Innovation
This is how SoClean 3+ utilizes powerful Ozone Stream technology to reduce 99.9% of bacteria in CPAP accessories.*

Ozone Facts
Ozone is a gas made up of three oxygen atoms (O3). It exists in two main parts of Earth's atmosphere: the stratosphere and near the ground. In the stratosphere, ozone forms a layer that protects life on Earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun. Without this ozone layer, harmful UV radiation would cause serious health problems, such as skin cancer and cataracts.
Near or on Earth’s ground, ozone is used in various industries such as water treatment, air purification, and more because of its ability to reduce bacteria.*
Sources:
Ozone works primarily through its powerful oxidizing properties. When ozone (O3) comes into contact with contaminants like bacteria or viruses, it oxidizes them. This process involves the ozone molecule breaking apart and transferring an oxygen atom to the contaminants, altering their structure and rendering them harmless.
In the atmosphere, ozone absorbs ultraviolet (UV) radiation, protecting living organisms from its harmful effects. It undergoes a cycle of breaking down and reforming, constantly absorbing and scattering UV rays, which is crucial for shielding life on Earth from radiation-induced damage.
Sources:
Ozone is safe when used appropriately, but its safety depends on a number of factors including the concentration and location in which it is present.
However, ozone has beneficial uses, particularly in bacterial reduction* in water treatment, air purification, and even in food industries, without leaving harmful residues. When used carefully in controlled environments and at proper concentrations, ozone is a safe and effective tool.
Sources:
In the Food & Beverage industry, ozone is widely used for bacterial reduction in water, bottles & packaging, and safe and effective preservation of some foods.
In the Hospitality industry, ozone is used by hotels and resorts as a quick and reliable tool for odor removal, as well as fighting bacteria on room surfaces.
In the Health and Medical field, ozone is used in the laundering of linens to boost the cleanliness of fabric for maximum patient safety. It is also used as a means for whole-room bacterial reduction.
General Information
Ozone General Information
What Is Ozone? Definition and Facts
Introduction to Ozone
Food & Beverage Industry
Food Processing
Food & Beverage Safety
Food Production
Hospitality
Air Treatment and Odor Control
Sanitation and Odor Control
Case Study - Hotels
Medical and Healthcare
Ozone in Health
Ozone & PPE
What is Ozone and how is it used in hospitals?
Water Treatment
Ozone and water treatment
Ozone and drinking water disinfection
Various Applications
*†Ozone's disinfecting capability is dependent on a number of factors including but not limited to: its concentration, duration of exposure, method of application, and environmental conditions.
References: 1. NASA 2. NASA 3. Oxidation Technology 4. National Library of Medicine




